Sand detection ML
Sand detection ML
The framework of the project was to develop a Machine Learning (ML) based model for one of our clients in the oil & gas industry to qualitatively identify sand production events by classifying signals created by sand particles and other sources.
Sand production is a major risk for safe and economical operations. The failure to develop an accurate sand production models costs the oil and gas industry significant resources to either repair or reinstall well equipment. The identification of a sand event in real-time is not trivial. The most reliable way to detect sand events precisely would be sampling and further laboratory measurements. However, this cannot be done on field with hundreds of wells continuously and at any time. An alternative option is to monitor the well with non-intrusive acoustic sand detector (ASD), which, among any other existing signals, measures the noise of collision of sand particles with pipe wall in an elbow.
ASD signal is interference of multiples acoustic sources. Complexity requires development of advance algorithms to eliminate abundant false notifications of conventional. False notifications can occur due to change in flow regime, choke, gas lift rate, or environmental noises. Laboratory works also prove that detection of sand events by acoustic detectors is very complicated process and gave motivation for application of machine and deep learning methodologies in the scope of this study.
The study focused on detecting sand production events using machine learning techniques in an oil field. Events with sand concentration above 5 pptb were considered as sand events. The data ware collected from wells with various petrophysical properties, and the dataset included parameters such as pressure, choke, and acoustic detector signals. The training and testing dataset was prepared with labeled samples for sand and no-sand events and statistical features were extracted from the labeled data.
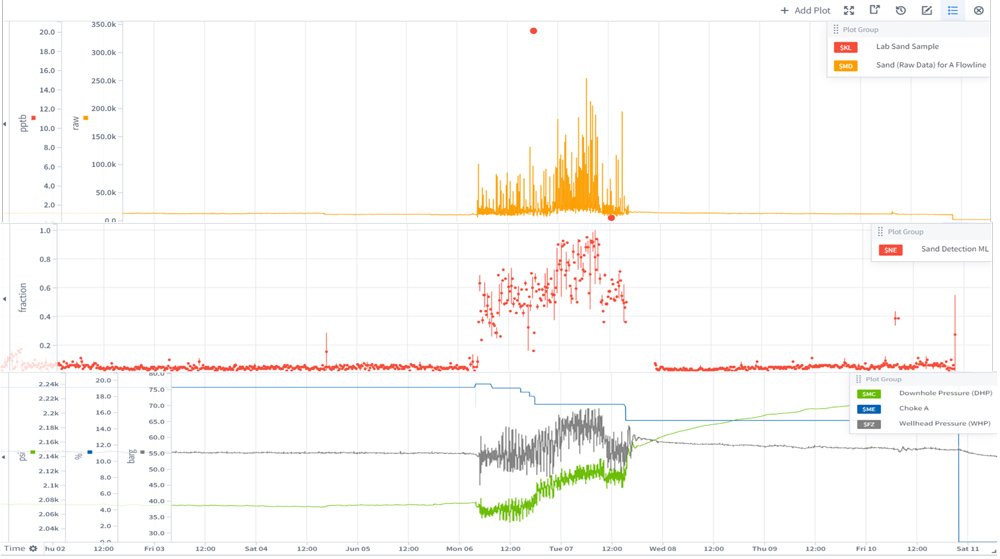
Different machine learning algorithms were examined. The results illustrate that the decision tree based ensemble models were the ones that have the highest accuracy. The selected Random Forest Classifier model was tested on 16 wells for 332 sand event and the accuracy of the RFC model was 76.8%.
There are numerous advantages of using ML algorithm. ML algorithm helps to handle high number of the wells (e.g. 100+ wells for a given field) simultaneously. It is unbiased data driven methodology based on historical events. ML algorithm can recognize data-inherited “unseen” tendencies and enhances sand monitoring capability for petroleum engineers. It also increases reliability of acoustic sand detector when used together.